Pulses are defined as dried edible seeds of cultivated legumes. Pulses occupy an important place in the human diet. The demand for pulses is fast increasing; both in developed and developing countries, where they meet the minimum protein requirements of an increasing population turning to a vegetarian diet. The potential and prospect as a source of income and its capacity to generate household income were low due to the lack of appropriate splitting machines and the farmer's offer for the market simply without splitting. To solve the above problem evaluating a JAERC-developed soya bean grinding machine for pulses splitting is needed. The machine is comprised of three main units- a power transmission unit, a grinding unit, and a delivery unit beside the frame. The maximum splitting capacity (414.40 kg/hr and 418.41 kg/hr) was obtained at the operation speed of 500 rpm and 7 kg/min feeding rate for beans and peas respectively. The maximum splitting efficiency of the machine (93.15% and 97.26%) was recorded at a feeding rate of 6 kg/min and 500 rpm of the operated speed for the beans and peas respectively. The performance of the machine was significantly affected by the feeding rate and speed of the operation. Splitting efficiency, in general, increased when increasing the speed of the operation and decreased when increasing the feeding rate. The broken percentage of the pulse increases, when the speed of the disc increases and decreases as the feeding rate increases for each pulse. The splitting capacity of the machine increases as both the feeding rate and operating speed increase for each crop. The evaluated machine was good for peas and beans at 500 disc speed and a feeding rate of 7 kg/min. The machine needs further modification for better splitting purposes.
| Published in | American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management (Volume 10, Issue 1) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11 |
| Page(s) | 1-5 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Efficiency, Pulses, Splitting
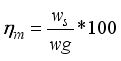
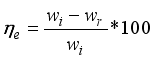
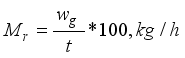
Feeding rate (kg/min) | Speed (rpm) | Capacity (kg/hr) | Efficiency (%) | Breakage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
6 | 300 | 349.68f | 84.23e | 2.24e |
400 | 351.00e | 87.05c | 3.51c | |
500 | 355.14c | 93.15a | 4.20a | |
7 | 300 | 407.36d | 82.33f | 1.52f |
400 | 411.42b | 85.04d | 3.08d | |
500 | 414.40a | 92.54b | 4.14b | |
CV | 0.55 | 0.77 | 6.29 | |
LSD(0.05) | 2.07 | 1.11 | 0.37 |
Feeding rate (kg/min) | Speed (rpm) | Capacity (kg/hr) | Efficiency (%) | Breakage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
6 | 300 | 352.16f | 91.26e | 1.53e |
400 | 355.77d | 94.14c | 2.13c | |
500 | 357.93c | 97.26a | 2.61a | |
7 | 300 | 411.30e | 89.96f | 1.01f |
400 | 415.69b | 93.20d | 1.82d | |
500 | 418.41a | 96.72b | 2.51b | |
CV | 0.28 | 0.73 | 0.75 | |
LSD(0.05) | 1.68 | 1.14 | 0.03 |
CV | Coefficient of Variation |
LSD | Least Significant Difference |
| [1] | Jiang, 2012. The design of the automatic mill. J. Agric. Mech. Res., 34(7): 157-160. |
| [2] | Kiber, H., T. Öztürk, 2011. Physical and mechanical properties of soybean. Int. Agrophysics, 22: 239-244. |
| [3] | Shukla, B. D., P. K. Srivastava, R. K. Gupta, 2014. Oilseed processing technology. Bhopal, India: Central Institute of Agricultural Engineering Publications. |
| [4] | Teressa D., Desta A., and Birtukan M. 2021. Development and Performance Evaluation of Engine Operated Pulses (Fababean, Pea and Lentil) splitting Machine. Omoia Agricultural Research Institute, (p. 269). Finfinne. |
| [5] | Uebersax MA, Cichy KA, Gomez FE, Porch TG, Heitholt J, Osorno JM, et al. Dry beans (phaseolus vulgaris L.) as a vital component of sustainable agriculture and food security-a review. Legume Science. 2023; 5(1): 1-13 |
| [6] | Williams S. and Akiko A. 2012. Special report on the history of soybean meal and modern soy oil. Unpublished manuscript on the history of soybeans and soy food Centre, Lafayette, California. |
| [7] | Wood, J. A. and Malcolmson, L. J., 2011. Tamworth Agricultural Institute, Industry & Investment NSW, Calala, NSW, Australia. Pulse Foods: Processing, Quality and Nutraceutical Applications, p. 193. |
APA Style
Bona, H. B., Berhanu, T., Wakeyo, T. (2025). Evaluation of Soya Bean Grinding Machine for Pulse Splitting. American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 10(1), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11
ACS Style
Bona, H. B.; Berhanu, T.; Wakeyo, T. Evaluation of Soya Bean Grinding Machine for Pulse Splitting. Am. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2025, 10(1), 1-5. doi: 10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11
@article{10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11,
author = {Husen Bona Bona and Tolosa Berhanu and Teshome Wakeyo},
title = {Evaluation of Soya Bean Grinding Machine for Pulse Splitting
},
journal = {American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management},
volume = {10},
number = {1},
pages = {1-5},
doi = {10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ajetm.20251001.11},
abstract = {Pulses are defined as dried edible seeds of cultivated legumes. Pulses occupy an important place in the human diet. The demand for pulses is fast increasing; both in developed and developing countries, where they meet the minimum protein requirements of an increasing population turning to a vegetarian diet. The potential and prospect as a source of income and its capacity to generate household income were low due to the lack of appropriate splitting machines and the farmer's offer for the market simply without splitting. To solve the above problem evaluating a JAERC-developed soya bean grinding machine for pulses splitting is needed. The machine is comprised of three main units- a power transmission unit, a grinding unit, and a delivery unit beside the frame. The maximum splitting capacity (414.40 kg/hr and 418.41 kg/hr) was obtained at the operation speed of 500 rpm and 7 kg/min feeding rate for beans and peas respectively. The maximum splitting efficiency of the machine (93.15% and 97.26%) was recorded at a feeding rate of 6 kg/min and 500 rpm of the operated speed for the beans and peas respectively. The performance of the machine was significantly affected by the feeding rate and speed of the operation. Splitting efficiency, in general, increased when increasing the speed of the operation and decreased when increasing the feeding rate. The broken percentage of the pulse increases, when the speed of the disc increases and decreases as the feeding rate increases for each pulse. The splitting capacity of the machine increases as both the feeding rate and operating speed increase for each crop. The evaluated machine was good for peas and beans at 500 disc speed and a feeding rate of 7 kg/min. The machine needs further modification for better splitting purposes.
},
year = {2025}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Evaluation of Soya Bean Grinding Machine for Pulse Splitting AU - Husen Bona Bona AU - Tolosa Berhanu AU - Teshome Wakeyo Y1 - 2025/06/23 PY - 2025 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11 DO - 10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11 T2 - American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management JF - American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management JO - American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management SP - 1 EP - 5 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2575-1441 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251001.11 AB - Pulses are defined as dried edible seeds of cultivated legumes. Pulses occupy an important place in the human diet. The demand for pulses is fast increasing; both in developed and developing countries, where they meet the minimum protein requirements of an increasing population turning to a vegetarian diet. The potential and prospect as a source of income and its capacity to generate household income were low due to the lack of appropriate splitting machines and the farmer's offer for the market simply without splitting. To solve the above problem evaluating a JAERC-developed soya bean grinding machine for pulses splitting is needed. The machine is comprised of three main units- a power transmission unit, a grinding unit, and a delivery unit beside the frame. The maximum splitting capacity (414.40 kg/hr and 418.41 kg/hr) was obtained at the operation speed of 500 rpm and 7 kg/min feeding rate for beans and peas respectively. The maximum splitting efficiency of the machine (93.15% and 97.26%) was recorded at a feeding rate of 6 kg/min and 500 rpm of the operated speed for the beans and peas respectively. The performance of the machine was significantly affected by the feeding rate and speed of the operation. Splitting efficiency, in general, increased when increasing the speed of the operation and decreased when increasing the feeding rate. The broken percentage of the pulse increases, when the speed of the disc increases and decreases as the feeding rate increases for each pulse. The splitting capacity of the machine increases as both the feeding rate and operating speed increase for each crop. The evaluated machine was good for peas and beans at 500 disc speed and a feeding rate of 7 kg/min. The machine needs further modification for better splitting purposes. VL - 10 IS - 1 ER -